
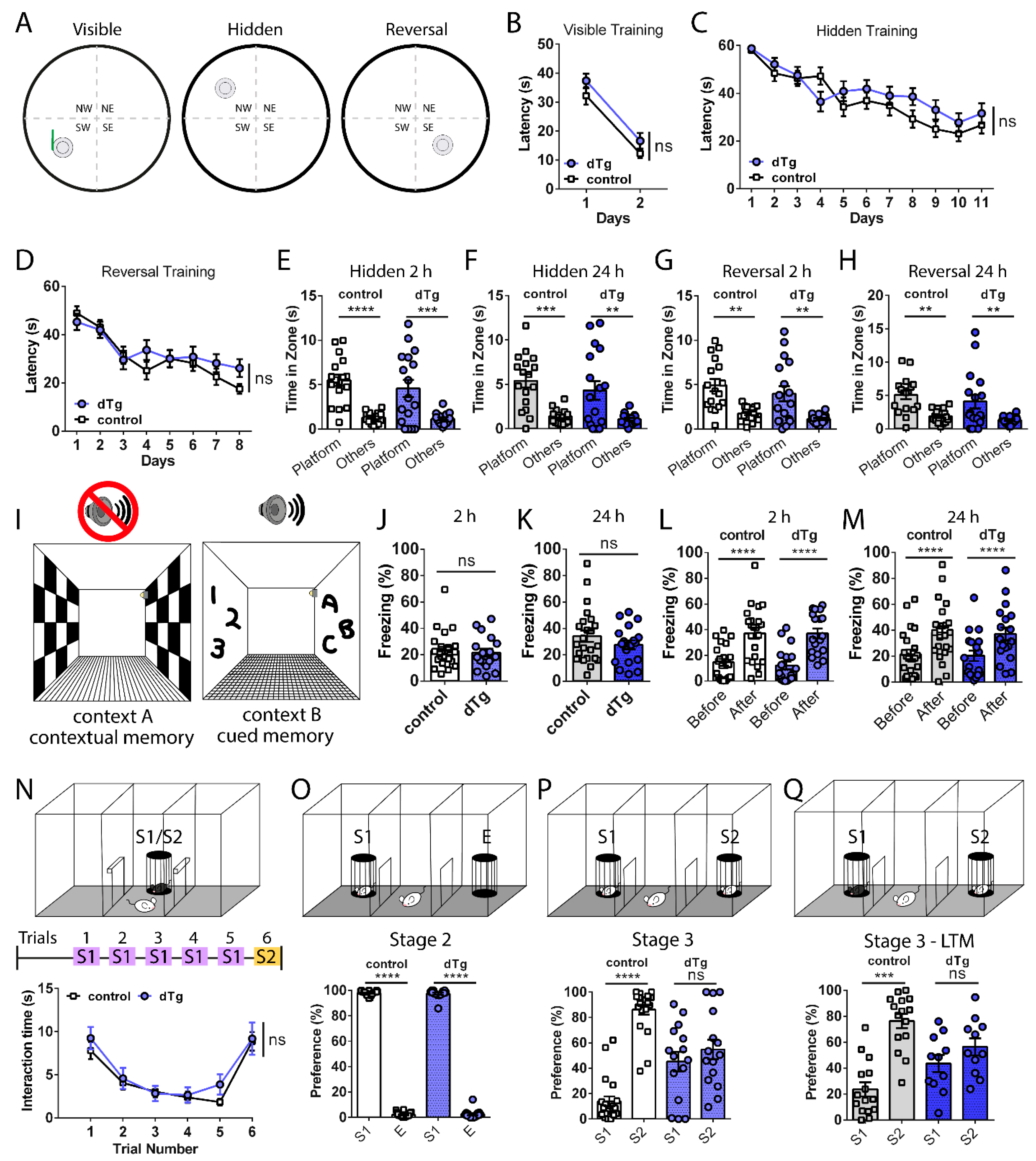
Biomarkers directly or indirectly relevant to the histopathology of AD, such as blood and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers, along with PET ligands are highly valuable in this scenario ( Dubois et al., 2014). Therefore, timely and accurate diagnosis is critical for the development of treatments for the initial stages of AD. Carriers of mutations associated with familial autosomal-dominant AD are known to develop subtle cognitive deficits <25 years before they develop dementia ( Mondadori et al., 2006 Mosconi et al., 2006). However, in some cases, these impairments develop into Alzheimer's disease (AD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that is neuropathologically characterized by extracellular senile plaques, formed by amyloid-β (Aβ) accumulation and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles, composed of a hyperphosphorylated microtubule-associated protein called tau ( Ashe and Zahs, 2010 Tarawneh and Holtzman, 2012). These findings indicate the significance of subtle intermediate readouts as early indicators of conditions such as Alzheimer's disease.īehavioral impairments lacking prominent clinical symptoms can be indicative of normal aging or mild cognitive impairment. Individual APP/PS1 mice preferred a non-cognitive search strategy called circling, which led to abrupt learning transitions and an increased number of unsuccessful trials.
#How to make mwm traces in any maze trial
However, with repeated trial and error, learning in APP/PS1 reached levels comparable to that of the wild-type mice during the later days of training. APP/PS1 mice displayed a higher number of unsuccessful trials during the initial days of training, unlike their wild-type counterparts. In this study, we used an alternative method to analyze the behavior of mice, aiming to gain a better understanding of the nature of cognitive deficits by focusing on the unsuccessful trials during water maze learning rather than on the successful ones. Conventional behavioral analysis using this model indicates that spatial memory is intact at 2 months of age. Using the APPswe/PS1dE9 (APP/PS1) mouse model of Alzheimer's disease, we utilized the Morris water maze spatial learning paradigm to systematically evaluate mild behavioral deficits that occur during the early stages of disease pathogenesis.
Mild behavioral deficits, which are part of normal aging, can be early indicators of an impending Alzheimer's disease.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
